Determining the right high bay lighting mounting height is crucial for optimal illumination in large spaces. At PacLights, we understand how this decision impacts energy efficiency, worker productivity, and overall lighting quality.
This guide will walk you through the key factors to consider when selecting the ideal mounting height for your high bay fixtures. We’ll also share practical tips to help you avoid common pitfalls in the process.
What Impacts High Bay Lighting Height?
Ceiling Height: The Foundation
The ceiling height of your facility forms the basis of your mounting decision. For spaces with ceilings 20 feet or higher, mount lights at 15-20 feet. If your ceiling reaches 30-40 feet, try a mounting height of 20-25 feet. For structures with ceilings above 40 feet, position your lights at 25-35 feet for optimal coverage.
Fixture Type: A Key Consideration
The type of high bay fixture you select significantly influences the ideal mounting height. UFO high bays, known for their compact design and high lumen output, often require higher mounting than their linear counterparts. Linear high bays, with their broader beam angle, can provide effective illumination at lower heights, offering wider coverage.
Light Distribution: Eliminating Shadows and Hotspots
Light distribution plays a vital role in creating uniform illumination across your space. The beam angles and optics of your fixtures are essential here. A wider beam angle provides broader coverage, which allows for more uniform illumination. This consideration helps prevent dark spots or overly bright areas that can disrupt workflow.
Task-Specific Needs: Customizing Light for Work
Different tasks require varied lighting solutions. In a warehouse setting, you might need brighter, more focused lighting for picking areas compared to general storage spaces. Assembly lines often require a minimum of 50 foot-candles of light, which impacts your mounting height decision. Always consider the specific activities in each area of your facility when determining the optimal mounting height for your high bay lights.
Future Flexibility: Planning for Change
When deciding on mounting height, consider potential future changes in your facility’s layout or operations. A flexible mounting system allows for easy adjustments (if needed) without major renovations. This foresight can save time and resources in the long run.

The next step in optimizing your high bay lighting involves calculating the precise mounting height for your specific space. Let’s explore the methods and tools that can help you achieve the perfect balance of illumination and efficiency.
How to Calculate Optimal Mounting Height
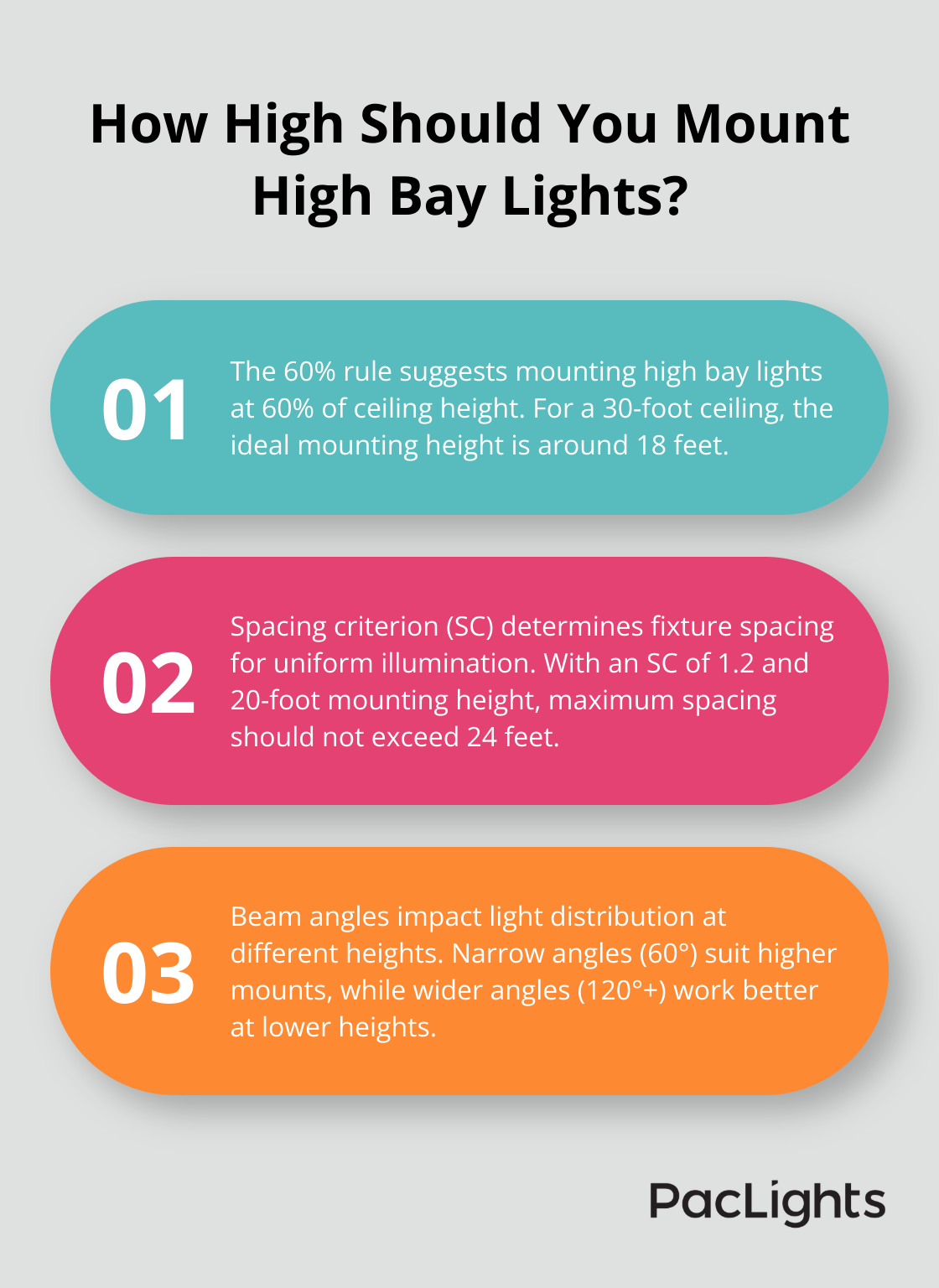
The 60% Rule: A Starting Point
A common approach in the industry is the 60% rule. This guideline suggests you mount high bay lights at approximately 60% of the ceiling height. For example, in a warehouse with a 30-foot ceiling, the ideal mounting height would be around 18 feet. However, this rule serves only as a starting point and requires adjustments based on specific requirements and fixture characteristics.
Spacing Criterion for Uniform Illumination
To achieve uniform lighting, use the spacing criterion (SC) method. Manufacturers typically provide the SC, which indicates the maximum ratio of spacing to mounting height for uniform illumination. For instance, if a fixture has an SC of 1.2 and you mount it at 20 feet, the maximum spacing between fixtures should not exceed 24 feet (20 x 1.2).
Beam Angle and Light Spread Considerations
The beam angle of your high bay fixtures significantly impacts light distribution. Narrow beam angles (around 60°) suit higher mounting heights, while wider angles (120° or more) work better at lower heights. In a 40-foot high facility, you can use fixtures with a 60° beam angle mounted at 30 feet to provide focused illumination for specific work areas.
Accounting for Environmental Factors
When you calculate mounting height, consider the specific needs of your space. Factors like surface reflectivity, wall and floor colors, and the presence of machinery or racking systems all influence the optimal height. Professional lighting design software can help account for these variables and provide more accurate calculations.
Real-World Testing
While calculations provide a solid foundation, real-world testing proves invaluable. Set up a small test area with adjustable mounting heights to fine-tune your lighting plan before full implementation. This approach ensures you achieve the best possible lighting solution for your specific environment.
Proper calculation of mounting height forms the foundation of an effective lighting plan. However, even with precise calculations, you might encounter common pitfalls. Let’s explore these potential issues and how to avoid them in the next section.
What Are Common Mounting Height Mistakes?
Overlooking Obstructions and Equipment
Many people fail to account for obstructions in the space when determining mounting height for high bay lighting. Tall machinery, storage racks, or suspended equipment can interfere with light distribution if not considered during the calculation. In a warehouse with 30-foot ceilings and 20-foot-high racking systems, mounting lights at 25 feet might seem logical. However, this could create shadows and dark spots in crucial work areas.

To prevent this issue, conduct a thorough site survey before you finalize your mounting height. Map out all potential obstructions and adjust your lighting plan accordingly. You might need to lower some fixtures or use a combination of mounting heights to ensure uniform illumination throughout the space.
Disregarding Glare and Visual Comfort
Glare is a significant concern in industrial and commercial settings, often overlooked when people focus solely on light output. Mounting high bay lights too low can create uncomfortable glare for workers, leading to eye strain and reduced productivity. Conversely, mounting them too high might reduce glare but could compromise light levels at the work surface.
To strike the right balance, consider the nature of tasks performed in the space. For areas with computer screens or precision work, try to minimize direct glare. Use glare shields or choose fixtures with appropriate optics to control light distribution. The Illuminating Engineering Society (IES) recommends maintaining a minimum angle of 30 degrees between the line of sight and the light source to reduce glare effectively.
Failing to Plan for Future Changes
The layout and use of industrial spaces often evolve over time. If you neglect to consider potential future changes when determining mounting height, you might face costly adjustments down the line. For example, a manufacturing facility might rearrange production lines or introduce new equipment, altering lighting requirements.
To future-proof your lighting setup, opt for adjustable mounting solutions where possible. This flexibility allows for easy height adjustments without major renovations. Additionally, consider slightly over-specifying your lighting system (this approach provides a buffer for future changes and ensures your lighting remains effective even if space utilization shifts).
Ignoring Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a significant role in determining the optimal mounting height for high bay lighting. Factors such as ambient temperature, humidity, and dust levels can impact the performance and lifespan of lighting fixtures. In environments with high ceilings (40 feet or more), the heat generated by fixtures can accumulate near the ceiling, potentially affecting their longevity.
To address these issues, consider using fixtures designed for specific environmental conditions. For instance, in facilities with high temperatures or humidity, choose fixtures with appropriate IP ratings. In dusty environments, select fixtures with sealed optics to prevent accumulation of particles on the light source.
Neglecting Light Quality and Color Rendering
While achieving adequate light levels is important, the quality of light and its ability to render colors accurately are equally critical factors often overlooked when determining mounting height. Mounting lights too high can result in poor color rendering and reduced visual acuity, especially in tasks requiring color discrimination or fine detail work.
To ensure optimal light quality, consider the Color Rendering Index (CRI) of your chosen fixtures and how it might be affected by mounting height. Try to maintain a balance between achieving uniform illumination and preserving the quality of light at the task level. In some cases, you might need to supplement general lighting with task-specific fixtures to maintain both light levels and quality.
Determining the optimal high bay lighting mounting height requires careful consideration of multiple factors. Ceiling height, fixture type, light distribution, and task-specific needs all play vital roles in creating an effective lighting solution. Professional lighting design proves invaluable in navigating these complexities and avoiding common pitfalls.

At PacLights, we offer expert guidance to help you make informed decisions about your high bay lighting installation. Our team considers all aspects of your space to develop a lighting solution that meets your current needs and adapts to future requirements. We take into account potential changes in your facility’s layout or operations.
Proper mounting height for high bay lighting yields significant benefits in energy efficiency and productivity. It provides optimal illumination with minimal energy waste, which translates to lower operational costs and a reduced carbon footprint. Well-planned lighting also enhances worker comfort and performance by reducing glare and eye strain (leading to improved productivity and fewer errors).






Disclaimer: PacLights is not responsible for any actions taken based on the suggestions and information provided in this article, and readers should consult local building and electrical codes for proper guidance.