Effective parking lot lighting is a critical aspect of urban infrastructure, impacting safety, security, and energy efficiency. At PacLights, we understand the importance of well-designed illumination systems for these spaces.
This guide explores essential parking lot lighting design guidelines, covering everything from regulatory compliance to fixture selection. We’ll help you navigate the complexities of creating a lighting plan that enhances visibility, reduces energy consumption, and promotes a safer environment for all users.
What Are Parking Lot Lighting Requirements?
Safety and Security: The Primary Concern
Safety stands as the cornerstone of parking lot lighting design. Adequate illumination reduces accident risks and deters criminal activity. The Illuminating Engineering Society (IES) recommends a minimum of 1 foot-candle throughout parking areas, with higher levels at entrances and exits. These guidelines ensure that drivers can safely navigate the lot and pedestrians can clearly see their surroundings.
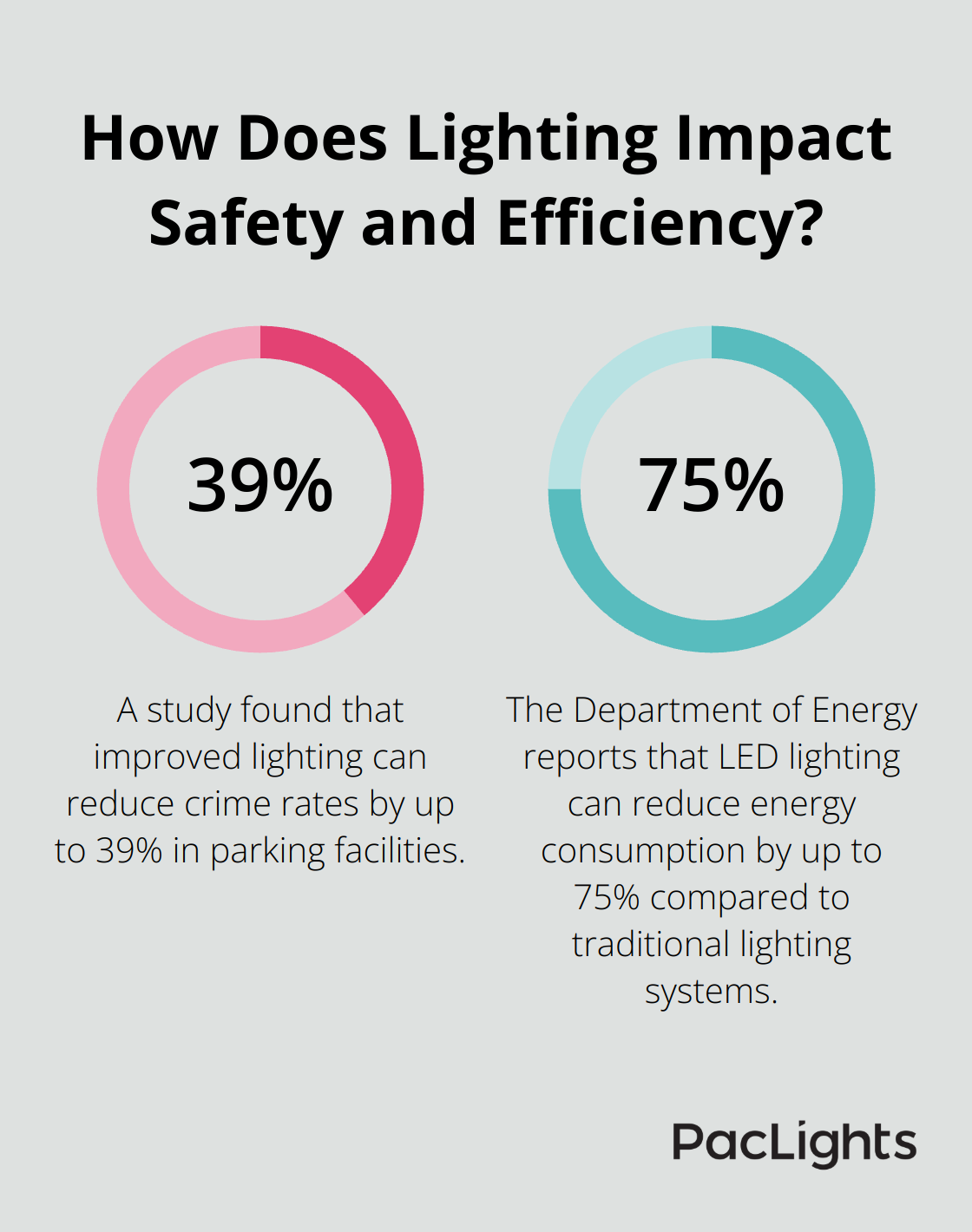
Proper lighting also enhances the effectiveness of security cameras. A well-lit parking lot allows for clearer footage, creating a synergy between lighting and surveillance systems that results in a safer environment for all users.
Navigating Local Regulations and Standards
Local regulations often dictate specific requirements for parking lot lighting. These may include maximum light levels, curfew times, and restrictions on light trespass. Some municipalities limit light levels at property boundaries to prevent light pollution affecting neighboring properties.
The International Dark-Sky Association (IDA) provides guidelines to minimize light pollution. Their recommendations include the use of fully shielded fixtures and limiting the correlated color temperature (CCT) of LED lights. Adherence to these standards not only ensures compliance but also demonstrates environmental responsibility.
Balancing Energy Efficiency and Performance
Energy efficiency plays a critical role in modern lighting design. LED technology has revolutionized parking lot lighting, offering significant energy savings compared to traditional lighting sources.
Smart controls further enhance energy efficiency. Occupancy sensors can dim lights in low-traffic areas, while photocells ensure lights operate only when natural light is insufficient. These strategies can lead to additional energy savings.
Optimizing Light Distribution and Uniformity
Effective parking lot lighting requires optimal light distribution and uniformity. This ensures that all areas of the lot receive adequate illumination without creating harsh contrasts or dark spots. Proper fixture placement and selection are key to achieving this balance.
Light uniformity ratios (the ratio of maximum to minimum light levels) should typically not exceed 4:1 for parking areas. This creates a consistent lighting environment that enhances visibility and safety for both drivers and pedestrians.
Considering Color Temperature and Rendering
The color temperature and rendering of parking lot lights significantly impact visibility and user comfort. Cool white light improves visibility and alertness, making it ideal for parking lots. However, warmer temperatures may be preferred in residential areas to minimize light pollution and create a more inviting atmosphere.
Color rendering index (CRI) is another important factor. A high CRI ensures that colors appear more natural under artificial light, aiding in vehicle identification and overall visual clarity.
As we move forward, let’s explore the key components that make up an effective parking lot lighting design, building on these fundamental requirements.
Mastering Light Distribution for Optimal Parking Lot Safety
Uniform Illumination: The Foundation of Safety
Uniform lighting eliminates dark spots and shadows that compromise safety. The Illuminating Engineering Society (IES) recommends a maximum-to-minimum uniformity ratio of 4:1 for parking areas. This means the brightest spot should not exceed four times the brightness of the darkest spot.

To achieve this, space light fixtures evenly and use appropriate optics. Type III distribution illuminates parking aisles effectively, while Type V works well for open areas. Photometric analysis software optimizes fixture placement and predicts light levels across the lot.
Color Temperature: Balancing Visibility and Comfort
Color temperature impacts visibility and user comfort significantly. Cool white light (4000K-5000K) enhances contrast and improves depth perception in parking lots. However, warmer temperatures (3000K-4000K) suit areas near residential zones to minimize light pollution and create a softer ambiance.
The color rendering index (CRI) plays an equally important role. Lighting with a high Color Rendering Index (CRI) of 80 or above helps cameras capture more accurate colors, which can be vital for identifying vehicles or enhancing overall safety. Many municipalities now require a minimum CRI for outdoor lighting installations.
Glare Reduction: Enhancing Safety and Comfort
Glare causes discomfort and temporarily impairs vision, posing a safety risk. Full cut-off fixtures direct light downward and prevent upward light spill, effectively combating this issue. The Illuminating Engineering Society recommends a maximum of 500 lumens above 90 degrees for parking lot fixtures.
Mitigating Light Pollution: Environmental Responsibility
Light pollution affects neighboring properties and disrupts local ecosystems. The International Dark-Sky Association suggests using fixtures with a BUG (Backlight, Uplight, Glare) rating of U0 to eliminate uplight completely. Dimming controls reduce light levels during off-peak hours, further minimizing environmental impact while maintaining safety.
Smart Controls: Optimizing Efficiency and Safety
Implementing smart controls (such as occupancy sensors and photocells) enhances both efficiency and safety. These systems adjust light levels based on real-time conditions, ensuring adequate illumination when needed while conserving energy during low-traffic periods.
The next chapter will explore the various types of fixtures available for parking lot lighting, including LED options and their specific advantages in this application.
Selecting Optimal Fixtures for Parking Lots
LED Technology: The Superior Choice
LED fixtures revolutionize parking lot lighting with unparalleled energy efficiency. These lights perform better than HPS luminaires in terms of power quality and energy savings. Their impressive lifespan slashes maintenance costs. LEDs also turn on instantly, eliminating warm-up times and enabling seamless integration with smart control systems.
Area Lights: The Parking Lot Workhorses
Area lights form the backbone of effective parking lot illumination. These fixtures typically feature rectangular or square designs and provide wide, even light distribution. Type III or Type V light distribution patterns work best for parking lots. Type III offers a wider lateral spread (perfect for illuminating aisles), while Type V creates a circular pattern (ideal for open areas).
Flood Lights: Targeted Illumination
Flood lights excel at accent lighting or illuminating specific features within parking lots. These fixtures produce a focused beam of light, making them perfect for highlighting signage or building facades. Adjustable flood lights allow precise targeting of particular areas that require extra attention.
Pole-Mounted Options: Height Matters
Pole-mounted fixtures remain the standard for parking lot lighting. The pole height plays a key role in light distribution and uniformity. Poles typically range from 20 to 40 feet, with taller poles allowing wider spacing and fewer fixtures overall. (Always check local regulations, as they may limit pole heights.)

When selecting pole-mounted fixtures, consider the wind load rating (especially important in areas prone to severe weather). Match the fixture’s EPA (Effective Projected Area) with the pole’s load capacity to ensure long-term stability and safety.
Smart Controls: Efficiency Meets Functionality
Smart controls take parking lot lighting to new levels of efficiency and functionality. Photocells ensure lights operate only when natural light is insufficient. Motion sensors dim or brighten lights based on activity levels. More advanced systems (like networked lighting controls) enable remote monitoring and management of lighting infrastructure. These systems provide valuable data on energy usage, detect malfunctions, and can integrate with other smart city technologies.
When implementing smart controls, analyze the specific needs of your parking lot. A retail parking lot might benefit from scheduled dimming during off-hours, while a 24-hour facility might require more consistent illumination (with strategic use of motion sensors in low-traffic areas).
Final Thoughts
Effective parking lot lighting design requires careful consideration of safety, energy efficiency, and regulatory compliance. Property owners and managers must understand the specific needs of their parking areas and select the right combination of fixtures, light distribution patterns, and control systems. LED technology has transformed outdoor lighting, offering superior energy efficiency, longevity, and performance.

Professional planning and installation prove essential for optimal results. Experts conduct thorough site analyses, create detailed photometric plans, and ensure compliance with local regulations (including parking lot lighting design guidelines). They also help navigate the complexities of new technologies and integration with existing systems.
At PacLights, we offer a range of lighting solutions tailored to diverse parking lot needs. Our products combine LED technology with advanced control options, allowing for customized, efficient, and effective illumination strategies. We provide the tools and expertise needed to create safe, efficient, and visually appealing parking environments.






Disclaimer: PacLights is not responsible for any actions taken based on the suggestions and information provided in this article, and readers should consult local building and electrical codes for proper guidance.